Europe - EU transition to a low-carbon economy
Lead Partners: Wageningen Research, Radboud University
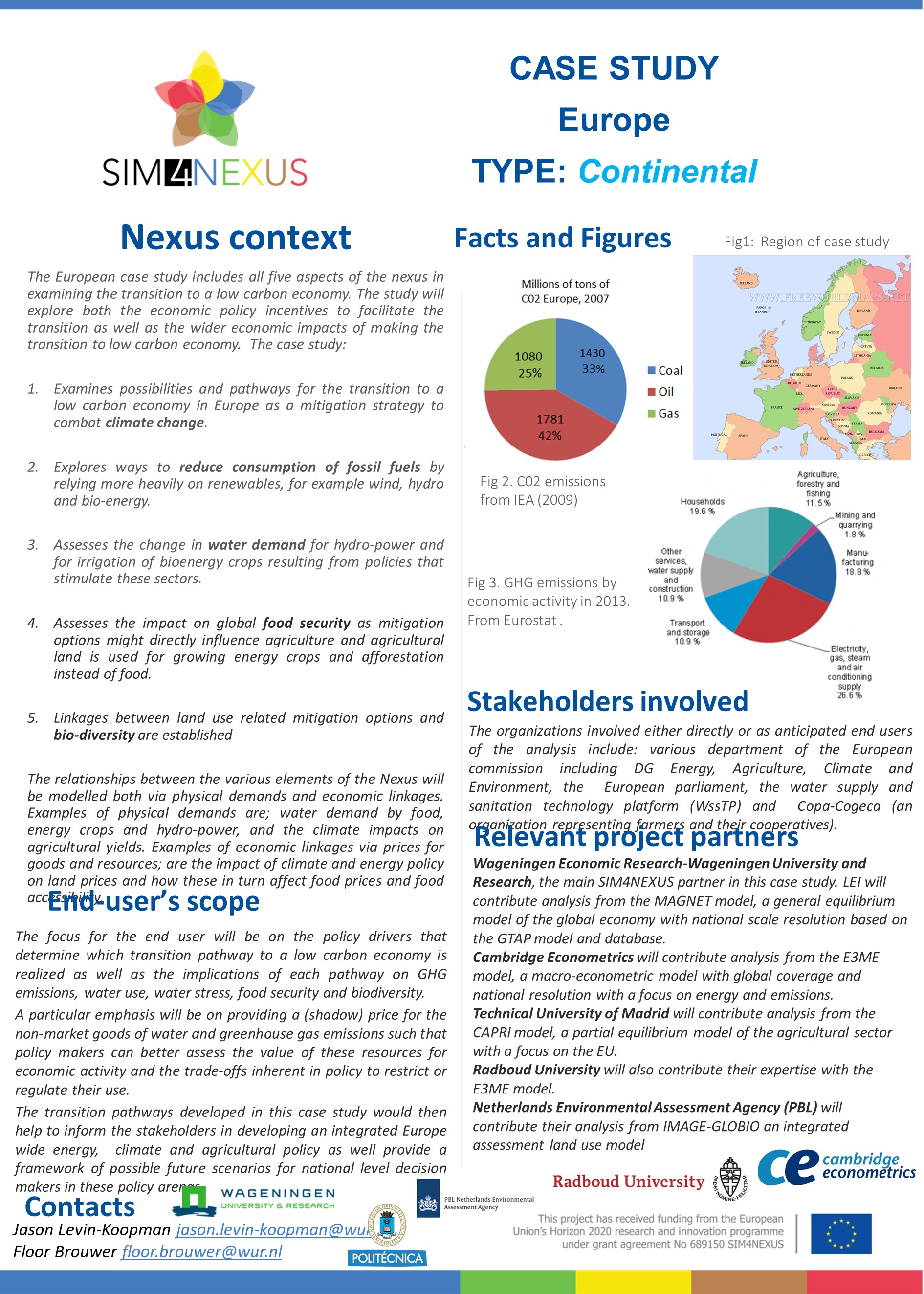
The essentials: Energy saving, energy efficiency & changing human diets.
Findings
• Raising resource-efficiency awareness with consumers stimulates a healthy diet and the purchase of energy-saving technologies. This strategy will help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining lower energy and food prices rather than by putting the obligation solely on the producers of energy and food.
• Bio-electricity combined with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology is an important component in the low-carbon economy transition, particularly in Eastern Europe. However, a large amount of bio-electricity can have an impact on land use for nature and agriculture.
• A large increase in renewable energy can increase energy prices and land use. Energy efficiency and savings are then central to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while limiting the amount of renewable energy needed to replace fossil fuels.
• Healthy diets with less meat consumption and food waste combined with an agriculture carbon tax are in line with climate goals and
will lead to more resource-efficient agriculture in Europe.
• A policy that encourages flexible land use and incentives to mitigate greenhouse gases in European agriculture can increase crop production for human consumption even with an increased burden of mitigation.
Crop farmers can use some land and other resources unused in a smaller livestock sector. However, increased cropland use might
increase water usage as it is often more water- intensive, e.g., irrigation in Southern Europe.
Click here for more information
For more information please contact:
Jason LEVIN-KOOPMAN
Wageningen Research
jason.levin-koopman@wur.nl